In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Tutte graph is a 3-regular graph with 46 vertices and 69 edges named after W. T. Tutte.[1] It has chromatic number 3, chromatic index 3, girth 4 and diameter 8.
| Tutte graph | |
|---|---|
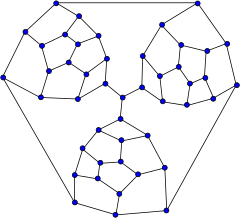 Tutte graph | |
| Named after | W. T. Tutte |
| Vertices | 46 |
| Edges | 69 |
| Radius | 5 |
| Diameter | 8 |
| Girth | 4 |
| Automorphisms | 3 (Z/3Z) |
| Chromatic number | 3 |
| Chromatic index | 3 |
| Properties | Cubic Planar Polyhedral |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
The Tutte graph is a cubic polyhedral graph, but is non-hamiltonian. Therefore, it is a counterexample to Tait's conjecture that every 3-regular polyhedron has a Hamiltonian cycle.[2]
Published by Tutte in 1946, it is the first counterexample constructed for this conjecture.[3] Other counterexamples were found later, in many cases based on Grinberg's theorem.
Construction edit
From a small planar graph called the Tutte fragment, W. T. Tutte constructed a non-Hamiltonian polyhedron, by putting together three such fragments. The "compulsory" edges of the fragments, that must be part of any Hamiltonian path through the fragment, are connected at the central vertex; because any cycle can use only two of these three edges, there can be no Hamiltonian cycle.
The resulting graph is 3-connected and planar, so by Steinitz' theorem it is the graph of a polyhedron. It has 25 faces.
It can be realized geometrically from a tetrahedron (the faces of which correspond to the four large nine-sided faces in the drawing, three of which are between pairs of fragments and the fourth of which forms the exterior) by multiply truncating three of its vertices.
Algebraic properties edit
The automorphism group of the Tutte graph is Z/3Z, the cyclic group of order 3.
The characteristic polynomial of the Tutte graph is :
Related graphs edit
Although the Tutte graph is the first 3-regular non-Hamiltonian polyhedral graph to be discovered, it is not the smallest such graph.
In 1965 Lederberg found the Barnette–Bosák–Lederberg graph on 38 vertices.[4][5] In 1968, Grinberg constructed additional small counterexamples to the Tait's conjecture – the Grinberg graphs on 42, 44 and 46 vertices.[6] In 1974 Faulkner and Younger published two more graphs – the Faulkner–Younger graphs on 42 and 44 vertices.[7]
Finally Holton and McKay showed there are exactly six 38-vertex non-Hamiltonian polyhedra that have nontrivial three-edge cuts. They are formed by replacing two of the vertices of a pentagonal prism by the same fragment used in Tutte's example.[8]
References edit
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Tutte's Graph". MathWorld.
- ^ Tait, P. G. (1884), "Listing's Topologie", Philosophical Magazine, 5th Series, 17: 30–46. Reprinted in Scientific Papers, Vol. II, pp. 85–98.
- ^ Tutte, W. T. (1946), "On Hamiltonian circuits" (PDF), Journal of the London Mathematical Society, 21 (2): 98–101, doi:10.1112/jlms/s1-21.2.98.
- ^ Lederberg, J. "DENDRAL-64: A System for Computer Construction, Enumeration and Notation of Organic Molecules as Tree Structures and Cyclic Graphs. Part II. Topology of Cyclic Graphs." Interim Report to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Grant NsG 81-60. December 15, 1965. [1].
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Barnette-Bosák-Lederberg Graph". MathWorld.
- ^ Grinberg, E. J. "Plane Homogeneous Graphs of Degree Three without Hamiltonian Circuits." Latvian Math. Yearbook, Izdat. Zinatne, Riga 4, 51–58, 1968.
- ^ Faulkner, G. B. and Younger, D. H. "Non-Hamiltonian Cubic Planar Maps." Discrete Math. 7, 67–74, 1974.
- ^ Holton, D. A.; McKay, B. D. (1988), "The smallest non-Hamiltonian 3-connected cubic planar graphs have 38 vertices", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 45 (3): 305–319, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(88)90075-5.