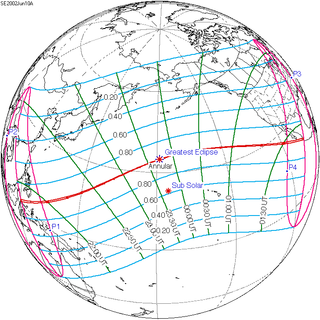
An annular solar eclipse occurred on Monday, June 10, 2002. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Indonesia, Palau (Kayangel Atoll), Northern Mariana on June 11 (Tuesday), and the western tip of Jalisco, Mexico, on June 10 (Monday). This eclipse was during the 2002 FIFA World Cup. The closest apogee occurred on June 4, 2002. It was the first annular solar eclipse visible in the Pacific in 6 months.
| Solar eclipse of June 10, 2002 | |
|---|---|
 Partial from Los Angeles, California | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.1993 |
| Magnitude | 0.9962 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 23 s (0 min 23 s) |
| Coordinates | 34°30′N 178°36′W / 34.5°N 178.6°W |
| Max. width of band | 13 km (8.1 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 23:45:22 |
| References | |
| Saros | 137 (35 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9513 |
It was partially visible in some areas of the United States; in Ventura, in southern California, some observation stations were set up for public viewing.[1] In Palm Desert, in the Coachella Valley, it was clearly visible, and it "got dark, it got cool, and it got eerie".[2]A "solar eclipse party" in Fresno drew around 400 attendees,[3] and as far north as Napa Valley, dozens of people went outside to watch the eclipse.,[4] and it was visible in Utah.[5] Canada's National Post predicted a "substantial crowd" for Vancouver, despite the eclipse there being less than 60%;[6] even in Victoria, where the eclipse was as low as 30%, dozens attended a show at the Dominion Astrophysical Observatory.[7]
Images edit
Related eclipses edit
Eclipses of 2002 edit
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on May 26.
- An annular solar eclipse on June 10.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on June 24.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on November 20.
- A total solar eclipse on December 4.
Tzolkinex edit
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of April 29, 1995
- Followed: Solar eclipse of July 22, 2024
Half-Saros edit
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of June 4, 1993
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of June 15, 2011
Tritos edit
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of July 11, 1991
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 10, 2013
Solar Saros 137 edit
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of May 30, 1984
- Followed: Solar eclipse of June 21, 2020
Inex edit
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of June 30, 1973
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 21, 2031
Solar eclipses 2000–2003 edit
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[8]
Partial solar eclipses on February 5, 2000 and July 31, 2000 occur in the previous lunar year set.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | 2000 July 01 Partial (south) |
−1.28214 | 122 | 2000 December 25 Partial (north) |
1.13669 | |
| 127 Totality from Lusaka, Zambia |
2001 June 21 Total |
−0.57013 | 132 Partial from Minneapolis, MN |
2001 December 14 Annular |
0.40885 | |
| 137 Partial from Los Angeles, CA |
2002 June 10 Annular |
0.19933 | 142 Totality from Woomera |
2002 December 04 Total |
−0.30204 | |
| 147 Culloden, Scotland |
2003 May 31 Annular |
0.99598 | 152 | 2003 November 23 Total |
−0.96381 | |
Saros 137 edit
It is a part of Saros cycle 137, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 70 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on May 25, 1389. It contains total eclipses from August 20, 1533, through December 6, 1695, first set of hybrid eclipses from December 17, 1713, through February 11, 1804, first set of annular eclipses from February 21, 1822, through March 25, 1876, second set of hybrid eclipses from April 6, 1894, through April 28, 1930, and second set of annular eclipses from May 9, 1948, through April 13, 2507. The series ends at member 70 as a partial eclipse on June 28, 2633. The longest duration of totality was 2 minutes, 55 seconds on September 10, 1569. Solar Saros 137 has 55 umbral eclipses from August 20, 1533, through April 13, 2507 (973.62 years). That's almost 1 millennium!
| Series members 30–40 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
| April 17, 1912 |
April 28, 1930 |
May 9, 1948 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
| May 20, 1966 |
May 30, 1984 |
June 10, 2002 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
| June 21, 2020 |
July 2, 2038 |
July 12, 2056 |
| 39 | 40 | |
| July 24, 2074 |
August 3, 2092 | |
Tritos series edit
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| December 21, 1805 (Saros 119) |
November 19, 1816 (Saros 120) |
October 20, 1827 (Saros 121) | |
| September 18, 1838 (Saros 122) |
August 18, 1849 (Saros 123) |
July 18, 1860 (Saros 124) | |
| June 18, 1871 (Saros 125) |
May 17, 1882 (Saros 126) |
April 16, 1893 (Saros 127) | |
| March 17, 1904 (Saros 128) |
February 14, 1915 (Saros 129) |
January 14, 1926 (Saros 130) | |
| December 13, 1936 (Saros 131) |
November 12, 1947 (Saros 132) |
October 12, 1958 (Saros 133) | |
| September 11, 1969 (Saros 134) |
August 10, 1980 (Saros 135) |
July 11, 1991 (Saros 136) | |
| June 10, 2002 (Saros 137) |
May 10, 2013 (Saros 138) |
April 8, 2024 (Saros 139) | |
| March 9, 2035 (Saros 140) |
February 5, 2046 (Saros 141) |
January 5, 2057 (Saros 142) | |
| December 6, 2067 (Saros 143) |
November 4, 2078 (Saros 144) |
October 4, 2089 (Saros 145) | |
| September 4, 2100 (Saros 146) |
|||
In the 22nd century:
- Solar saros 147: annular solar eclipse of August 4, 2111
- Solar saros 148: total solar eclipse of July 4, 2122
- Solar saros 149: total solar eclipse of June 3, 2133
- Solar saros 150: annular solar eclipse of May 3, 2144
- Solar saros 151: annular solar eclipse of April 2, 2155
- Solar saros 152: total solar eclipse of March 2, 2166
- Solar saros 153: annular solar eclipse of January 29, 2177
- Solar saros 154: annular solar eclipse of December 29, 2187
- Solar saros 155: total solar eclipse of November 28, 2198
In the 23rd century:
- Solar saros 156: annular solar eclipse of October 29, 2209
- Solar saros 157: annular solar eclipse of September 27, 2220
- Solar saros 158: total solar eclipse of August 28, 2231
- Solar saros 159: partial solar eclipse of July 28, 2242
- Solar saros 160: partial solar eclipse of June 26, 2253
- Solar saros 161: partial solar eclipse of May 26, 2264
- Solar saros 162: partial solar eclipse of April 26, 2275
- Solar saros 163: partial solar eclipse of March 25, 2286
- Solar saros 164: partial solar eclipse of February 22, 2297
Metonic series edit
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events, progressing from south to north between June 10, 1964, and August 21, 2036 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 10–11 | March 27–29 | January 15–16 | November 3 | August 21–22 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
| June 10, 1964 |
March 28, 1968 |
January 16, 1972 |
November 3, 1975 |
August 22, 1979 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
| June 11, 1983 |
March 29, 1987 |
January 15, 1991 |
November 3, 1994 |
August 22, 1998 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
| June 10, 2002 |
March 29, 2006 |
January 15, 2010 |
November 3, 2013 |
August 21, 2017 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
| June 10, 2021 |
March 29, 2025 |
January 14, 2029 |
November 3, 2032 |
August 21, 2036 |
References edit
- ^ "Eclipse observation station being set up in Grant Park today". Ventura County Star. Ventura, California. 2002-06-10. p. 11. Retrieved 2023-10-15 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Velush, Lukas (2002-06-11). "Solar phenomenon awes local residents". The Desert Sun. p. 11. Retrieved 2023-10-24 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Yahaira Castro (2002-06-11). "Discovery Center's solar eclipse party proves popular". The Fresno Bee.
- ^ Roseann Langlois (2002-06-11). "Solar eclipse covers Napa Valley". The Napa Valley Register.
- ^ "Solar eclipse tonight last to be visible in Utah for 10 years". The Daily Spectrum. Saint George, Utah. 2002-06-10. p. 1. Retrieved 2023-10-15 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "West will have best view of solar eclipse". National Post. Ontario, Canada. 2002-06-10. p. 2. Retrieved 2023-10-15 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Gerard Young (2002-06-11). "Celestial show draws curious". Times Colonist. Victoria, British Columbia.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links edit
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
Photos:
- A Partial Eclipse Over the Golden Gate Bridge, APOD June 12, 2002
- Photos and videos of annular solar eclipse (Japanese)
- Spaceweather.com: June 10, 2002 solar eclipse