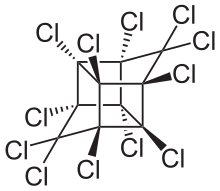
Mirex is an organochloride that was commercialized as an insecticide and later banned because of its impact on the environment. This white crystalline odorless solid is a derivative of cyclopentadiene. It was popularized to control fire ants but by virtue of its chemical robustness and lipophilicity it was recognized as a bioaccumulative pollutant. The spread of the red imported fire ant was encouraged by the use of mirex, which also kills native ants that are highly competitive with the fire ants. The United States Environmental Protection Agency prohibited its use in 1976.[1] It is prohibited by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dodecachlorooctahydro-1H-1,3,4-(epimethanetriyl)cyclobuta[cd]pentalene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.452 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | D008917 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10Cl12 | |
| Molar mass | 545.55 g/mol |
| Melting point | 485 °C (905 °F; 758 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Production and applications edit
Mirex was first synthesized in 1946,[2] but was not used in pesticide formulations until 1955. Mirex was produced by the dimerization of hexachlorocyclopentadiene in the presence of aluminium chloride.
Mirex is a stomach insecticide, meaning that it must be ingested by the organism in order to poison it. The insecticidal use was focused on Southeastern United States to control the imported fire ants Solenopsis saevissima richteri and Solenopsis invicta. Approximately 250,000 kg of mirex was applied to fields between 1962 and 1975 (US NRC, 1978). Most of the mirex was in the form of "4X mirex bait", which consists of 0.3% mirex in 14.7% soybean oil mixed with 85% corncob grits. Application of the 4X bait was designed to give a coverage of 4.2 g mirex/ha and was delivered by aircraft, helicopter or tractor. 1x and 2x bait were also used. Use of mirex as a pesticide was banned in 1978. The Stockholm Convention banned production and use of several persistent organic pollutants, and mirex is one of the "dirty dozen".[3]
Degradation edit
Characteristic of chlorocarbons, mirex does not burn easily; combustion products are expected to include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen chloride, chlorine, phosgene, and other organochlorine species. Slow oxidation produces chlordecone ("Kepone"), a related insecticide that is also banned in most of the western world, but more readily degraded. Sunlight degrades mirex primarily to photomirex (8-monohydromirex) and later partly to 2,8-dihydromirex.[1][4][5]
-
Photomirex
-
2,8-dihydromirex
Mirex is highly resistant to microbiological degradation. It only slowly dechlorinates to a monohydro derivative by anaerobic microbial action in sewage sludge and by enteric bacteria. Degradation by soil microorganisms has not been described.
Bioaccumulation and biomagnification edit
Mirex is highly cumulative and amount depends upon the concentration and duration of exposure. There is evidence of accumulation of mirex in aquatic and terrestrial food chains to harmful levels. After 6 applications of mirex bait at 1.4 kg/ha, high mirex levels were found in some species; turtle fat contained 24.8 mg mirex/kg, kingfishers, 1.9 mg/kg, coyote fat, 6 mg/kg, opossum fat, 9.5 mg/kg, and racoon fat, 73.9 mg/kg. In a model ecosystem with a terrestrial-aquatic interface, sorghum seedlings were treated with mirex at 1.1 kg/ha. Caterpillars fed on these seedlings and their faeces contaminated the water which contained algae, snails, Daphnia, mosquito larvae, and fish. After 33 days, the ecological magnification value was 219 for fish and 1165 for snails.
Although general environmental levels are low, it is widespread in the biotic and abiotic environment. Being lipophilic, mirex is strongly adsorbed on sediments.
Safety edit
Mirex is only moderately toxic in single-dose animal studies (oral LD50 values range from 365–3000 mg/kg body weight).[6] It can enter the body via inhalation, ingestion, and via the skin. The most sensitive effects of repeated exposure in animals are principally associated with the liver, and these effects have been observed with doses as low as 1.0 mg/kg diet (0.05 mg/kg body weight per day), the lowest dose tested. At higher dose levels, it is fetotoxic (25 mg/kg in diet) and teratogenic (6.0 mg/kg per day). Mirex was not generally active in short-term tests for genetic activity. There is sufficient evidence of its carcinogenicity in mice and rats.[citation needed] Delayed onset of toxic effects and mortality is typical of mirex poisoning.[citation needed] Mirex is toxic for a range of aquatic organisms, with crustacea being particularly sensitive.
Mirex induces pervasive chronic physiological and biochemical disorders in various vertebrates. No acceptable daily intake (ADI) for mirex has been advised by FAO/WHO. IARC (1979) evaluated mirex's carcinogenic hazard and concluded that "there is sufficient evidence for its carcinogenicity to mice and rats. In the absence of adequate data in humans, based on above result it can be said, that it has carcinogenic risk to humans". Data on human health effects do not exist [citation needed].
Health effects edit
Per a 1995 ATSDR report mirex caused fatty changes in the livers, hyperexcitability and convulsion, and inhibition of reproduction in animals. It is a potent endocrine disruptor, interfering with estrogen-mediated functions such as ovulation, pregnancy, and endometrial growth. It also induced liver cancer by interaction with estrogen in female rodents.[7]
References edit
- ^ a b Robert L. Metcalf "Insect Control" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" Wiley-VCH, Wienheim, 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_263
- ^ H. J. Prins (1946). "Synthesis of Polychloro Compounds with Aluminium Chloride .XI.The Elimination of Hydrogen Chloride from Polychloro Compounds and the Formation of Cyclic Compounds -The Synthesis of Perchlorocyclopentadien". Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas. 65 (7–8): 455–467. doi:10.1002/recl.19460650607.
- ^ Kaiser KLE (1978). "Pesticide Report: The rise and fall of Mirex". Environmental Science and Technology. 12 (5): 520–528. Bibcode:1978EnST...12..520K. doi:10.1021/es60141a005.
- ^ IPCS International Programme on Chemical Safety: Mirex – Health and Safety Guide No. 39, 1990.
- ^ Kelly L. Lambrych, John P. Hassett: Wavelength-dependent photoreactivity of mirex in Lake Ontario, Environmental Science and Technology, 2006, 40(3), 858–863; doi:10.1021/es0511927.
- ^ EL-Bayomey AA, IW Somak, and S. Branch. Embryotoxicity of the pesticide Mirex In vitro. Teratogenesis, Carcinogenesis, and Mutagenesis 2002, 22:239-249.
- ^ Faroon O, Kueberuwa S, Smith L, DeRosa C (1995). "ATSDR evaluation of health effects of chemicals. II. Mirex and chlordecone: health effects, toxicokinetics, human exposure, and environmental fate". Toxicology and Industrial Health. 11 (6): 1–203. doi:10.1177/074823379501100601. PMID 8723616. S2CID 45676131.
See also edit
- Mirex in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- International Organization for the Management of Chemicals (IOMC), 1995, POPs Assessment Report, December.1995.
- Lambrych KL, and JP Hassett. Wavelength-Dependent Photoreactivity of Mirex in Lake Ontario. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 858-863
- Mirex Health and Safety Guide. IPCS International Program on Chemical Safety. Health and Safety Guide No.39. 1990
- Toxicological Review of Mirex. In support of summary information on the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) 2003. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington DC.