The list of parties to the Biological Weapons Convention encompasses the states which have signed and ratified or acceded to the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC), a multilateral treaty outlawing biological weapons.
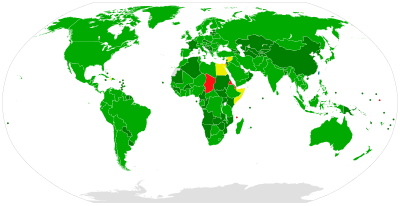
| Signed and ratified Acceded or succeeded Unrecognized state, abiding by treaty | Only signed Non-signatory |
On 10 April 1972, the BWC was opened for signature. The Netherlands became the first state to deposit their signature of the treaty that same day. The treaty closed for signature upon coming into force on 26 March 1975 with the deposit of ratification by 22 states. Since then, states that did not sign the BWC can only accede to it.
A total of 197 states may become members of the BWC, including all 193 United Nations member states, the Cook Islands, the Holy See, the State of Palestine and Niue. As of February 2023, 185 states have ratified or acceded to the treaty, most recently South Sudan in February 2023.[1] As well, the Republic of China (Taiwan), which is currently only recognized by 11 UN member states, deposited their instruments of ratification of the BWC with the United States government prior to the US's decision to switch their recognition of the sole legitimate government of China from the Republic of China (ROC) to the People's Republic of China (PRC). A further five states have signed but not ratified the treaty.
Several countries made reservations when ratifying the agreement declaring that it did not imply their complete satisfaction that the BWC allows the stockpiling of biological agents and toxins for "prophylactic, protective or other peaceful purposes", nor should it imply recognition of other countries they do not recognise.
States Parties edit
According to the treaties database maintained by the United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs, as of February 2023, 185 states have ratified or acceded to the BWC.[1] However, the status of the succession of a number of additional states to the BWC is unclear. For further details, see the Succession of colonies to the BWC section below.
Multiple dates indicate the different days in which states submitted their signature or deposition, varied by location. This location is noted by: (L) for London, (M) for Moscow, and (W) for Washington D.C.
| State[1][2][3][4] | Signed | Deposited | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 26, 1975 (L) | Ratification |
| Albania | Jun 3, 1992 (W) Aug 11, 1992 (L) Mar 26, 1993 (M) |
Accession | |
| Algeria | Sep 28, 2001 (W) | Accession | |
| Andorra | Mar 2, 2015 (W) | Accession | |
| Angola | Jul 26, 2016 (W) | Accession | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | Jan 29, 2003 (L) | Accession | |
| Argentina | Aug 1, 1972 (M) Aug 3, 1972 (L) Aug 7, 1972 (W) |
Nov 27, 1979 (W) Dec 5, 1979 (L) Dec 27, 1979 (M) |
Ratification |
| Armenia | Jun 7, 1994 (M, W) | Accession | |
| Australia | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Oct 5, 1977 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Austria | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Aug 10, 1973 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Azerbaijan | Feb 26, 2004 (M, W) | Accession | |
| Bahamas | Nov 26, 1986 (L) | Accession | |
| Bahrain | Oct 28, 1988 (L) | Accession | |
| Bangladesh | Mar 11, 1985 (M) Mar 12, 1985 (W) Mar 13, 1985 (L) |
Accession | |
| Barbados | Feb 16, 1973 (W) | Feb 16, 1973 (W) | Ratification |
| Belarus | Apr 10, 1972 (M) | Mar 26, 1975 (M) | Ratification as Byelorussian SSR |
| Belgium | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 15, 1979 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Belize | Oct 20, 1986 (L) Nov 25, 1986 (W) Jan 13, 1987 (M) |
Succession from United Kingdom | |
| Benin | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Apr 25, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| Bhutan | Jun 8, 1978 (W) | Accession | |
| Bolivia | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Oct 30, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Aug 15, 1994 (W) | Succession from SFR Yugoslavia | |
| Botswana | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Feb 5, 1992 (W) | Ratification |
| Brazil | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Feb 27, 1973 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Brunei | Jan 31, 1991 (L) | Accession | |
| Bulgaria | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Aug 2, 1972 (L) Sep 13, 1972 (W) Sep 19, 1972 (M) |
Ratification |
| Burkina Faso | Apr 17, 1991 (W) | Accession | |
| Burundi | Apr 10, 1972 (M, W) | Oct 18, 2011 (L) | Ratification |
| Cabo Verde | Oct 20, 1977 (M) | Accession | |
| Cambodia | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Mar 9, 1983 (W) | Ratification |
| Cameroon | Jan 18, 2013 (W) | Accession | |
| Canada | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Sep 18, 1972 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Central African Republic | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Sep 25, 2018 (W) | Ratification |
| Chile | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Apr 22, 1980 (L) | Ratification |
| China | Nov 15, 1984 (L, M, W) | Accession | |
| Colombia | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Dec 19, 1983 (W) | Ratification |
| Republic of the Congo | Oct 23, 1978 (W) | Accession | |
| Cook Islands | Dec 4, 2008 (L) | Accession | |
| Costa Rica | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Dec 17, 1973 (W) | Ratification |
| Côte d'Ivoire | May 23, 1972 (W) | Mar 23, 2016 (M) Apr 26, 2016 (L) |
Ratification |
| Croatia | Apr 28, 1993 (W) | Succession from SFR Yugoslavia[a] | |
| Cuba | Apr 12, 1972 (M) | Apr 21, 1976 (M) | Ratification |
| Cyprus | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) Apr 14, 1972 (M) |
Nov 6, 1973 (L) Nov 13, 1973 (W) Nov 21, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Czech Republic | Apr 5, 1993 (L) Apr 9, 1993 (M) Sep 29, 1993 (W) |
Succession from Czechoslovakia Signed 10 April 1972 Deposited 30 April 1973 | |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | Apr 10, 1972 (M, W) | Sep 16, 1975 (L) Jan 28, 1977 (W) |
Ratification as Zaire |
| Denmark | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 1, 1973 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Dominica | Aug 1, 2016 (L) | Succession[b] | |
| Dominican Republic | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Feb 23, 1973 (W) | Ratification |
| Ecuador | Jun 14, 1972 (W) | Mar 12, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| El Salvador | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Dec 31, 1991 (W) | Ratification |
| Equatorial Guinea | Jan 16, 1989 (M) Jul 29, 1992 (W) |
Accession | |
| Estonia | Jun 21, 1993 (W) Jul 1, 1993 (M) |
Accession | |
| Ethiopia | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | May 26, 1975 (L, M) Jun 26, 1975 (W) |
Ratification |
| Fiji | Feb 22, 1973 (L) | Sep 4, 1973 (W) Oct 1, 1973 (L) Oct 5, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Finland | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Feb 4, 1974 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| France | Sep 27, 1984 (L, M, W) | Accession | |
| Gabon | Apr 10, 1972 (L) | Aug 16, 2007 (W) | Ratification |
| Gambia | Jun 2, 1972 (M) Aug 8, 1972 (L) Nov 9, 1972 (W) |
May 7, 1997 (L) Jun 10, 1997 (M) Aug 1, 1997 (W) |
Ratification |
| Georgia | May 22, 1996 (L, M) | Accession | |
| Germany | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Apr 7, 1983 (L, W) | Ratification as West Germany Also ratified by East Germany on 28 November 1972 prior to German reunification |
| Ghana | Apr 10, 1972 (M, W) | Jun 6, 1975 (L) | Ratification |
| Greece | Apr 10, 1972 (L) Apr 12, 1972 (W) Apr 14, 1972 (M) |
Dec 10, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| Grenada | Oct 22, 1986 (L) | Accession | |
| Guatemala | May 9, 1972 (W) | Sep 19, 1973 (W) | Ratification |
| Guinea | Nov 9, 2016 (L)[c] | Accession | |
| Guinea-Bissau | Aug 20, 1976 (M) | Accession | |
| Guyana | Jan 3, 1973 (W) | Mar 26, 2013 (W) | Ratification |
| Holy See | Jan 7, 2002 (W) | Accession | |
| Honduras | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Mar 14, 1979 (W) | Ratification |
| Hungary | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Dec 27, 1972 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Iceland | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Feb 15, 1973 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| India | Jan 15, 1973 (L, M, W) | Jul 15, 1974 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Indonesia | Jun 20, 1972 (M, W) Jun 21, 1972 (L) |
Feb 4, 1992 (M) Feb 19, 1992 (L) Apr 1, 1992 (W) |
Ratification |
| Iran | Apr 10, 1972 (M, W) Nov 16, 1972 (L) |
Aug 22, 1973 (L, W) Aug 27, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Iraq | May 11, 1972 (M) | Jun 19, 1991 (M) | Ratification |
| Ireland | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) | Oct 27, 1972 (L, W) | Ratification |
| Italy | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | May 30, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Jamaica | Aug 13, 1975 (L) | Accession | |
| Japan | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Jun 8, 1982 (W) Jun 18, 1982 (L, M) |
Ratification |
| Jordan | Apr 10, 1972 (W) Apr 17, 1972 (L) Apr 24, 1972 (M) |
May 30, 1975 (M) Jun 2, 1975 (W) Jun 27, 1975 (L) |
Ratification |
| Kazakhstan | Jun 15, 2007 (M) | Accession | |
| Kenya | Jan 7, 1976 (L) | Accession | |
| Kuwait | Apr 14, 1972 (M, W) Apr 27, 1972 (L) |
Jul 18, 1972 (W) Jul 26, 1972 (L) Aug 1, 1972 (M) |
Ratification |
| Kyrgyzstan | Oct 15, 2004 (M) | Accession | |
| Laos | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 20, 1973 (M) Mar 22, 1973 (W) Apr 25, 1973 (L) |
Ratification |
| Latvia | Feb 6, 1997 (L) | Accession | |
| Lebanon | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) Apr 21, 1972 (M) |
Mar 26, 1975 (L) Apr 2, 1975 (M) Jun 13, 1975 (W) |
Ratification |
| Lesotho | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Sep 6, 1977 (L) | Ratification |
| Liberia | Apr 10, 1972 (W) Apr 14, 1972 (L) |
Nov 4, 2016 (W) | Ratification |
| Libya | Apr 10, 1972 (M) | Jan 19, 1982 (M) | Ratification |
| Liechtenstein | May 30, 1991 (W) May 31, 1991 (M) Jun 6, 1991 (L) |
Accession | |
| Lithuania | Feb 10, 1998 (L) | Accession | |
| Luxembourg | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M) Apr 12, 1972 (W) |
Mar 23, 1976 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Madagascar | Oct 13, 1972 (L) | Mar 7, 2008 (M, W) | Ratification |
| Malawi | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Apr 2, 2013 (W) | Ratification |
| Malaysia | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Sep 6, 1991 (L, M) Sep 26, 1991 (W) |
Ratification |
| Maldives | Aug 2, 1993 (M) | Accession | |
| Mali | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Nov 25, 2002 (W) | Ratification |
| Malta | Sep 11, 1972 (L) | Apr 7, 1975 (L) | Ratification |
| Marshall Islands | Nov 15, 2012 (W) | Accession | |
| Mauritania | Jan 28, 2015 (L) | Accession | |
| Mauritius | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Aug 7, 1972 (W) Jan 11, 1973 (L) Jan 15, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Mexico | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Apr 8, 1974 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Moldova | Jan 28, 2005 (M, W) | Accession | |
| Monaco | Apr 30, 1999 (L) | Accession | |
| Mongolia | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Sep 5, 1972 (W) Sep 14, 1972 (L) Oct 20, 1972 (M) |
Ratification |
| Montenegro | Jun 3, 2006 (M) Dec 12, 2006 (L) |
Succession from Serbia and Montenegro[d] | |
| Morocco | May 2, 1972 (L) May 3, 1972 (W) Jun 5, 1972 (M) |
Mar 21, 2002 (L) | Ratification |
| Mozambique | Mar 29, 2011 (L) | Accession | |
| Myanmar | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Dec 1, 2014 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Namibia | Feb 25, 2022 (L) | Accession | |
| Nauru | Mar 5, 2013 (W) | Accession | |
| Nepal | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Nov 4, 2016 (L, W) Nov 11, 2016 (M) |
Ratification |
| Kingdom of the Netherlands | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Jun 22, 1981 (L, M, W) | Ratification, for the whole Kingdom |
| New Zealand | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Dec 13, 1972 (W) Dec 18, 1972 (L) Jan 10, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Nicaragua | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) | Aug 7, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| Niger | Apr 21, 1972 (W) | Jun 23, 1972 (W) | Ratification |
| Nigeria | Jul 3, 1972 (M) Jul 10, 1972 (L) Dec 6, 1972 (W) |
Jul 3, 1973 (W) Jul 9, 1973 (L) Jul 20, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Niue | Jun 14, 2018 (W) | Accession | |
| North Korea | Mar 13, 1987 (M) | Accession | |
| North Macedonia | Dec 26, 1996 (M) Mar 14, 1997 (L) Apr 23, 1997 (W) |
Succession from SFR Yugoslavia[e] | |
| Norway | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Aug 1, 1973 (L, W) Aug 23, 1973 (M) |
Ratification |
| Oman | Mar 31, 1992 (W) | Accession | |
| Pakistan | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Sep 25, 1974 (M) Oct 3, 1974 (L, W) |
Ratification |
| Palau | Feb 20, 2003 (W) | Accession | |
| Palestine | Jan 9, 2018 (L, M) | Accession | |
| Panama | May 2, 1972 (W) | Mar 20, 1974 (W) | Ratification |
| Papua New Guinea | Oct 27, 1980 (L) Nov 13, 1980 (M) Mar 16, 1981 (W) |
Accession | |
| Paraguay | Jun 9, 1976 (W) | Accession | |
| Peru | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Jun 5, 1985 (L, M) Jun 11, 1985 (W) |
Ratification |
| Philippines | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) Jun 21, 1972 (M) |
May 21, 1973 (W) | Ratification |
| Poland | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Jan 25, 1973 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Portugal | Jun 29, 1972 (W) | May 15, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Qatar | Nov 14, 1972 (L) | Apr 17, 1975 (L) | Ratification |
| Romania | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Jul 25, 1979 (W) Jul 26, 1979 (L) Jul 27, 1979 (M) |
Ratification |
| Russia | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 26, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification as Soviet Union |
| Rwanda | Apr 10, 1972 (M, W) | May 20, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | Apr 2, 1991 (L) | Accession | |
| Saint Lucia | Nov 26, 1986 (L) | Succession from United Kingdom | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | May 13, 1999 (L) | Succession from United Kingdom | |
| Samoa | Sep 21, 2017 (W) | Accession | |
| San Marino | Sep 12, 1972 (W) Jan 30, 1973 (M) Mar 21, 1973 (L) |
Mar 11, 1975 (L) Mar 17, 1975 (W) Mar 27, 1975 (M) |
Ratification |
| Sao Tome and Principe | Aug 24, 1979 (M) | Accession | |
| Saudi Arabia | Apr 12, 1972 (W) | May 24, 1972 (W) | Ratification |
| Senegal | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Mar 26, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| Serbia | Apr 27, 1992 (M) Jun 5, 2001 (W) Jun 13, 2001 (L) |
Succession from SFR Yugoslavia Signed 10 April 1972 Deposited 25 October 1973[9] Succession from Serbia and Montenegro[f] | |
| Seychelles | Oct 11, 1979 (L) Oct 16, 1979 (W) Oct 24, 1979 (M) |
Accession | |
| Sierra Leone | Nov 7, 1972 (W) Nov 24, 1972 (L) |
Jun 29, 1976 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Singapore | Jun 19, 1972 (L, M, W) | Dec 2, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Slovakia | Jan 1, 1993 (M) May 17, 1993 (L) Jun 10, 1993 (W) |
Succession from Czechoslovakia Signed 10 April 1972 Deposited 30 April 1973 | |
| Slovenia | Apr 7, 1992 (L, M) Aug 20, 1992 (W) |
Succession from SFR Yugoslavia | |
| Solomon Islands | Jun 17, 1981 (L) | Succession from United Kingdom | |
| South Africa | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Nov 3, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| South Korea | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) | Jun 25, 1987 (L, W) | Ratification |
| South Sudan | Feb 15, 2023 (W) | Accession | |
| Spain | Apr 10, 1972 (L, W) | Jun 20, 1979 (L, W) | Ratification |
| Sri Lanka | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Nov 18, 1986 (L, M, W) | Ratification Signed as Ceylon |
| Sudan | Oct 17, 2003 (L) Oct 20, 2003 (M) Nov 7, 2003 (W) |
Accession | |
| Suriname | Jan 6, 1993 (L, M) Apr 9, 1993 (W) |
Accession | |
| Swaziland | Jun 18, 1991 (L) | Accession | |
| Sweden | Feb 27, 1974 (M) Feb 27, 1975 (L, W) |
Feb 5, 1976 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Switzerland | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | May 4, 1976 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Tajikistan | Jun 27, 2005 (M) | Accession | |
| Tanzania | Aug 16, 1972 (L) | Aug 14, 2019 (L) | Ratification |
| Thailand | Jan 17, 1973 (W) | May 28, 1975 (W) | Ratification |
| Timor-Leste | May 5, 2003 (W) | Accession | |
| Togo | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Nov 10, 1976 (W) | Ratification |
| Tonga | Sep 28, 1976 (L) | Accession | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | Jul 19, 2007 (L) | Accession | |
| Tunisia | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | May 18, 1973 (W) May 30, 1973 (M) Jun 6, 1973 (L) |
Ratification |
| Turkey | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Oct 25, 1974 (M) Nov 4, 1974 (L) Nov 5, 1974 (W) |
Ratification |
| Turkmenistan | Jan 11, 1996 (M) Mar 8, 1996 (W) |
Accession | |
| Uganda | May 12, 1992 (W) | Accession | |
| Ukraine | Apr 10, 1972 (M) | Mar 26, 1975 (M) | Ratification as Ukrainian SSR |
| United Arab Emirates | Sep 28, 1972 (L) | Jun 19, 2008 (L) [11] | Ratification |
| United Kingdom | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 26, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| United States | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M, W) | Mar 26, 1975 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Uruguay | Apr 6, 1981 (W) | Accession | |
| Uzbekistan | Jan 26, 1996 (M) | Accession | |
| Vanuatu | Sep 6, 2016 (L) | Succession[g] | |
| Venezuela | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Oct 18, 1978 (L, M, W) | Ratification |
| Vietnam | Apr 10, 1972 (M) | Jun 20, 1980 (M) | Ratification as the Socialist Republic of Vietnam Signed by the Democratic Republic of Vietnam and Republic of Vietnam on 10 April 1972 prior to Vietnamese reunification[12] |
| Yemen | Apr 26, 1972 (M) May 10, 1972 (L) |
Jun 1, 1979 (M) | Ratification as South Yemen Also signed by North Yemen on 10 April 1972 prior to Yemeni unification |
| Zambia | Jan 15, 2008 (L) | Accession | |
| Zimbabwe | Nov 5, 1990 (L) | Accession |
- Notes
- ^ Croatia's effective date of succession was 8 October 1991.[5]
- ^ Dominica's effective date of succession was 3 November 1978.[2]
- ^ The Chairman of the Meeting of the States Parties to the BWC reported that Guinea had submitted an instrument of accession in 2011 that the depositaries deemed to be legally insufficient to become a party to the treaty.[6]
- ^ Montenegro's effective date of succession was 3 June 2006.[7]
- ^ Macedonia's effective date of succession was 17 November 1991.[8]
- ^ The FR Yugoslavia's (later Serbia and Montenegro) effective date of succession from the SFR Yugoslavia was 27 April 1992, while Serbia's effective date of succession from Serbia and Montenegro was 3 June 2006.[10]
- ^ Vanuatu's effective date of succession was 30 July 1980.[2]
State with limited recognition, abiding by treaty edit
The Republic of China (Taiwan), which is currently only recognized by 11 UN member states, deposited their instruments of ratification of the BWC with the United States government prior to the US's decision to switch their recognition of the sole legitimate government of China from the Republic of China (ROC) to the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1971. When the PRC subsequently ratified the treaty, they described the ROC's ratification as "illegal". The ROC has committed itself to continue to adhere to the requirements of the treaty, and the United States has declared that they still consider them to be "bound by its obligations".[13]
| State | Signed | Deposited | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Republic of China | Apr 10, 1972 | Feb 9, 1973 | Ratification |
Signatory states edit
The following four states have signed, but not ratified the BWC.[14]
| State | Signed | Ratification status[a][14] |
|---|---|---|
| Egypt | Apr 10, 1972 (L, M) | No action expected in near future |
| Haiti | Apr 10, 1972 (W) | Waiting for further information, assistance, or have other priorities[b] |
| Somalia | Jul 3, 1972 (M) | Waiting for further information, assistance, or have other priorities |
| Syria | Apr 14, 1972 (M) | No action expected in near future |
- Notes
- ^ As per the 2023 Report of the Chairman on Universalization Activities to the Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction.
- ^ As of September 2017, a ratification bill has been approved by the Cabinet of Ministers and submitted to parliament.[15][16]
Non-signatory states edit
The following 8 UN member states have neither signed nor ratified the BWC.[14]
| State | Ratification status[a][14] |
|---|---|
| Chad | Waiting for further information, assistance, or have other priorities[b] |
| Comoros | Process well advanced[c] |
| Djibouti | Waiting for further information, assistance, or have other priorities[20] |
| Eritrea | Waiting for further information, assistance, or have other priorities |
| Israel | No action expected in near future |
| Kiribati[d] | Process started[e] |
| Micronesia | Process started[f] |
| Tuvalu[d] | Process started |
- Notes
- ^ As per the 2023 Report of the Chairman on Universalization Activities to the Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction.
- ^ Parliamentarians for Global Action reported in June 2017 that Chad's National Assembly had recommended the government ratify the agreement.[17][15]
- ^ In 2007, the Chairman of the Meeting of the States Parties to the BWC reported that ratification of the BWC had been approved by the government of Comoros pending signature by the President.[18][19] In October 2023, the BWC Implementation Support Unit and United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs reported that Comoros government officials had informed them that ratification would be brought forward to parliament during the current session.[14]
- ^ a b Neither Kiribati or Tuvalu are listed as parties to the BWC in documents from the Meetings of the States Parties to the BWC,[14] but their status is unclear. See succession of colonies to the BWC below.
- ^ Kiribati's Deputy Permanent Representative to the United Nations committed in 2016 to recommend accession to the treaty.[21] Accession is expected in 2020 according to Parliamentarians for Global Action.[22][needs update]
- ^ The Congress of the Federated States of Micronesia introduced a resolution approving ratification of the convention in June 2019.[23][24]
Succession of colonies to the BWC edit
The status of several former dependent territories of a state party to the BWC, whose administrating power ratified the Convention on their behalf, with regards to the Convention following their independence is currently unclear. According to the Vienna Convention on Succession of States in respect of Treaties (to which 22 states are party), "newly independent states" (a euphemism for former colonies) receive a "clean slate", such that the new state does not inherit the treaty obligations of the colonial power, but that they may join multilateral treaties to which their former colonizers were a party without the consent of the other parties in most circumstances. Conversely, in "cases of separation of parts of a state" (a euphemism for all other new states), the new state remains bound by the treaty obligations of the state from which they separated. To date, this Convention has only been ratified by 22 states.
The United Kingdom attached a territorial declaration to their instrument of ratification of the BWC in 1975 stating in part that it applied to:[25]
"... in respect of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Dominica and Territories under the territorial sovereignty of the United Kingdom, as well as the State of Brunei, the British Solomon Islands Protectorate and, within the limits of the United Kingdom jurisdiction therein, the Condominium of New Hebrides [subsequently renamed Vanuatu]."
This declaration bound the territories of Kiribati and Tuvalu to the terms of the Convention.[26] Following their independence, none of these states have made unambiguous declarations of succession to the BWC.[26] Dominica and Vanuatu's statuses were likewise ambiguous from their independence until 2016.
Kiribati edit
In 1979, Kiribati gained their independence and subsequently, the President of Kiribati sent a note to the UNSG stating that:[26]
... the Government of the Republic of Kiribati declares that, with regard to multilateral treaties applied or extended to the former Gilbert Islands, it will continue to apply the terms of each such treaty provisionally and on the basis of reciprocity until such time as it notifies the depositary authority of its decision with respect thereto.”
Since then, none of the depositaries for the BWC has received an instrument of accession or succession to the Convention from Kiribati.[1] However, the Government of Kiribati has made statements suggesting that it does not consider itself a party to the treaty.[26]
Tuvalu edit
Following independence in 1978, the Prime Minister of Tuvalu sent a note to the UNSC stating that:[26]
"The Government of Tuvalu desires that it should be presumed that each treaty purporting or deemed to bind Tuvalu before Independence has been legally succeeded to by Tuvalu and that action should be based on such presumption unless and until the Government of Tuvalu decides that any particular treaty should be treated as having lapsed."
Since then, none of the depositaries for the BWC has received an instrument of accession or succession to the Convention from Tuvalu.[1] However, the Government of Tuvalu has made statements suggesting that it does not consider itself a party to the treaty.[26]
Dominica edit
After becoming independent in 1978, the Prime Minister of Dominica sent a note to the Secretary-General of the United Nations (UNSG) stating that:[26]
“The Government of Dominica declares that, with regard to multilateral treaties applied or extended to the former British Associated State of Dominica, it will continue to apply such terms of each treaty provisionally and on the basis of reciprocity until such time as it notifies the depositary authority of its decision in respect thereof.”
The Government of Dominica later stated that it did not consider itself bound by the Convention.[26] However, Dominica was listed as a state party to the BWC in documents from the Meetings of the States Parties to the BWC.[19] The UK Treaty Office (as depositary) did not receive an instrument of succession from Dominica until 2016.[2]
Vanuatu edit
In 1980, the territory gained their independence. Vanuatu was listed as a state party to the BWC in documents from the Meetings of the States Parties to the BWC,[19] however the Government of Vanuatu made statements suggesting that it did not consider itself a party to the treaty[26] and the UK depositary had no record of receiving an instrument of succession to the BWC from Vanuatu until 2016.[26][27]
See also edit
- List of parties to the Chemical Weapons Convention
- List of parties to the Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons
- List of parties to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty
- List of parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons
- List of parties to the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
- List of parties to the Ottawa Treaty
- List of parties to the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
- List of parties to weapons of mass destruction treaties
References edit
- ^ a b c d e f "Disarmament Treaties Database: Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
- ^ a b c d "Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction". Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-01-04. Retrieved 2015-02-10.
"Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction". Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved 2019-04-27. - ^ "Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction". United States Department of State. 2018-10-09. Retrieved 2019-06-30.
- ^ Конвенция о запрещении разработки, производства и накопления запасов бактериологического (биологического) и токсинного оружия и об их уничтожении (in Russian). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia. 2013-04-17. Retrieved 2015-08-28.
- ^ "Croatia: Succession to Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-03-03.
- ^ "Status of universalization of the Convention" (PDF). Seventh Review Conference of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2011-10-10. Retrieved 2014-10-12.
- ^ "Montenegro: Succession to Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2016-08-10.
- ^ "North Macedonia: Succession to Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2019-03-12.
- ^ "Serbia: Succession to Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-03-03.
- ^ "Serbia: Succession to Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-03-03.
- ^ "UAE ratifies BWC". United Nations Office at Geneva. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- ^ "Viet Nam: Signature of Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-03-03.
- ^ "China: Accession to Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-03-03.
- ^ a b c d e f "Report on universalization activities". Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2019-10-08. Retrieved 2019-11-01.
- ^ a b "Report on universalization activities". Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2017-09-25. Retrieved 2019-11-01.
- ^ "Maigre bilan du Parlement : Près d'une vingtaine d'instruments internationaux en souffrance". 2018-11-19. Archived from the original on 2018-11-27. Retrieved 2018-11-26.
- ^ "Biological Weapons Disarmament Updates (June 2017)". Parliamentarians for Global Action. 2017-06-28. Archived from the original on 2017-08-19. Retrieved 2017-07-04.
- ^ "Report of the Chairman on universalization activities" (PDF). Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2007-12-11. Retrieved 2014-10-12.
- ^ a b c "Report on universalization activities" (PDF). Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2015-11-05. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-05-10. Retrieved 2017-10-31.
- ^ "Report on universalization activities1" (PDF). Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2021-09-23. Retrieved 2023-11-09.
- ^ "Eighth Review Conference of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction" (PDF). 2016-06-15. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-09-25. Retrieved 2017-09-25.
- ^ "Campaign for Universality and Implementation of the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC) & Implementation of UN Security Council Resolution 1540 (2004)". Parliamentarians for Global Action. Retrieved 2020-05-09.
- ^ "A Resolution" (PDF). 2019-06-13. Retrieved 2019-10-07.
- ^ "Report on universalization activities". Meeting of the States Parties to the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on Their Destruction. 2019-10-08. Retrieved 2019-11-01.
- ^ "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland: Ratification of Biological Weapons Convention". United Nations Office for Disarmament Affairs. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Building a Global Ban: Why States Have Not Joined the BWC" (PDF). BioWeapons Prevention Project. April 2009. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
- ^ "Council Decision CFSP/2016/51 of 18 January 2016 in support of the Biological Weapons Convention - Report -Regional workshop to promote the universalisation of the BWC in the Pacific" (PDF). 2017-07-28.