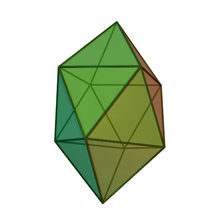
In geometry, the gyroelongated square bipyramid is a polyhedron with 16 triangular faces. it can be constructed from a square antiprism by attaching two equilateral square pyramids to each of its square faces. The same shape is also called hexakaidecadeltahedron[1], heccaidecadeltahedron,[2] or tetrakis square antiprism;[1] these last names mean a polyhedron with 16 triangular faces. It is an example of deltahedron, and of a Johnson solid.
| Gyroelongated square bipyramid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Gyroelongated bipyramid, Deltahedron, Johnson J16 – J17 – J18 |
| Faces | 16 triangles |
| Edges | 24 |
| Vertices | 10 |
| Vertex configuration | |
| Symmetry group | |
| Dual polyhedron | Truncated square trapezohedron |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |
The dual polyhedron of the gyroelongated square bipyramid is a square truncated trapezohedron with eight pentagons and two squares as its faces. The gyroelongated square pyramid appears in chemistry as the basis for the bicapped square antiprismatic molecular geometry, and in mathematical optimization as a solution to the Thomson problem.
Construction edit
Like other gyroelongated bipyramids, the gyroelongated square bipyramid can be constructed by attaching two equilateral square pyramids onto the square faces of a square antiprism; this process is known as gyroelongation.[3][4] These pyramids cover each square, replacing it with four equilateral triangles, so that the resulting polyhedron has 16 equilateral triangles as its faces. A polyhedron with only equilateral triangles as faces is called a deltahedron. There are only eight different convex deltahedra, one of which is the gyroelongated square bipyramid.[5] More generally, the convex polyhedron in which all faces are regular is the Johnson solid, and every convex deltahedron is a Johnson solid. The gyroelongated square bipyramid is numbered among the Johnson solids as .[6]
One possible system of Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a gyroelongated square bipyramid, giving it edge length 2, is:[1]
Properties edit
The surface area of a gyroelongated square bipyramid is 16 times the area of an equilateral triangle, that is:[4]
It has the same three-dimensional symmetry group as the square antiprism, the dihedral group of of order 8. Its dihedral angle is similar to the gyroelongated square pyramid, by calculating the sum of the equilateral square pyramid and the square antiprism's angle: the dihedral angle of two adjacent triangles in an equilateral square pyramid is , and that of square and triangle in the same pyramid is . The dihedral angle of a square antiprism between the two adjacent triangles is , and that between square and triangle is . The dihedral angle of the square and triangle, on the edge where the square pyramid attaches the antiprism, is .[7]
Dual polyhedron edit
The dual polyhedron of a gyroleongated square bipyramid is the square truncated trapezohedron.[citation needed] It has eight pentagons and two squares.[8]
Application edit
Gyroelongated square bipyramid can be visualized in the geometry of chemical compounds as the atom cluster surrounding a central atom as a polyhedron, and the compound of such cluster is the bicapped square antiprismatic molecular geometry.[9] It has 10 vertices and 24 edges, corresponding to the closo polyhedron with skeletal electrons. An example is nickel carbonyl carbide anion , a 22 skeletal electron chemical compound with ten vertices and the deficiency of two carbon monoxides.[10]
The Thomson problem concerning the minimum-energy configuration of charged particles on a sphere. The minimum solution known for places the points at the vertices of a gyroelongated square bipyramid, inscribed in a sphere.[1]
References edit
- ^ a b c d Sloane, N. J. A.; Hardin, R. H.; Duff, T. D. S.; Conway, J. H. (1995), "Minimal-energy clusters of hard spheres", Discrete & Computational Geometry, 14 (3): 237–259, doi:10.1007/BF02570704, MR 1344734, S2CID 26955765
- ^ Pugh, Anthony (1976), Polyhedron: A Visual Approach, University of California Press, p. 35.
- ^ Rajwade, A. R. (2001), Convex Polyhedra with Regularity Conditions and Hilbert's Third Problem, Texts and Readings in Mathematics, Hindustan Book Agency, doi:10.1007/978-93-86279-06-4, ISBN 978-93-86279-06-4.
- ^ a b c Berman, Martin (1971), "Regular-faced convex polyhedra", Journal of the Franklin Institute, 291 (5): 329–352, doi:10.1016/0016-0032(71)90071-8, MR 0290245.
- ^ Trigg, Charles W. (1978), "An Infinite Class of Deltahedra", Mathematics Magazine, 51 (1): 55–57, doi:10.2307/2689647, JSTOR 2689647.
- ^ Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, Zbl 0132.14603.
- ^ Francis, Darryl (August 2013), "Johnson solids & their acronyms", Word Ways, 46 (3): 177.
- ^ de Corato, Marzio; Prosperio, Davide M.; Bernasconi, Marco; Benedek, Giorgio (2013), "Two C28 Clathretes", in Diudea, Mircea Vasile; Nagy, Csaba Levente (eds.), Diamond and Related Nanostructures, Springer, p. 80–81, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-6371-5, ISBN 978-94-007-6371-5.
- ^ Remhov, Arndt; Černý, Radovan (2021), "Hydroborate as novel solid-state electrolytes", in Schorr, Susan; Weidenthaler, Claudia (eds.), Crystallography in Materials Science: From Structure-Property Relationships to Engineering, de Gruyter, p. 270, ISBN 978-3-11-067485-9.
- ^ King, R. Bruce (1993), Applications of Graph Theory and Topology in In Cluster and Coordination Chemistry, CRC Press, p. 102.

