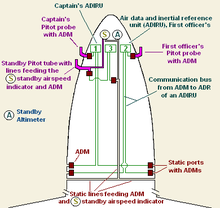
An air data module is a component of the navigation system.[1] Each unit converts pneumatic (air pressure) information from a pitot tube or a static port into numerical information which is sent on a data bus.[2] This pressure information is received and processed by the Air Data Reference (ADR) component of the Air Data Inertial Reference Unit (ADIRU).[1] This processed information is then sent to one or more display management computers that present information on the cockpit's primary flight display.[3] Airspeed information is also sent to the flight computers and other electronics,[4] including the autoflight subsystem (e.g. flight management and guidance system).[5]
Construction edit
The air data module is a gas pressure sensor which converts mechanical forces created by gas pressure into digital signals that can be carried to the air data reference unit. ADMs generally have a maintenance bus and communication bus, and a connector on the housing for a pressurized gas line that is connected to the pitot tube or static ports. The maintenance bus can be EIA-485 and the communication bus can be ARINC 429[2][6]
References edit
- ^ a b "Erroneous flight instruments". Boeing Aero Magazine, Issue 08. Archived from the original on 12 June 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ "SmartCockpit: A330 - Systems - Indicating and Recording". Archived from the original on 2007-01-15.
- ^ "SmartCockpit: A330 - Control systems". Archived from the original on 2009-06-12.
- ^ "SmartCockpit: A330 - Autoflight systems". Archived from the original on 2007-01-15.
- ^ "www51.honeywell.com" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03.